立陶宛
閱讀設定
立陶宛共和國 Lietuvos Respublika (立陶宛文) | |
|---|---|
國歌:Tautiška giesmė (《國歌》) | |
 立陶宛響歐洲嘅位置(紅色) | |
| 首都 同最大城市 | 維爾紐斯 54°41′N 25°19′E / 54.683°N 25.317°E |
| 官方語言 | 立陶宛語[1] |
| 族裔 (2021年[2]) | |
| 宗教 (2021年[3]) | |
| 政府 | 單一制半總統制共和國[4][5][6][7] |
• 總統 | 吉塔納斯·瑙塞達 |
• 總理 | 因格麗達·希莫尼特 |
• 國會議長 | 維多利亞·希米利特-尼爾森 |
| 立法機關 | 國會 |
| 成立 | |
• 個名已知嘅最早記載 | 1009年3月9號 |
• 立陶宛大公國 | 1236年 |
• 同波蘭組成共主邦聯 | 1386年2月2號 |
• 波蘭立陶宛聯邦成立 | 1569年7月1號 |
• 聯邦滅亡 | 1795年10月 |
• 宣佈獨立 | 1918年2月16號 |
• 恢復獨立 | 1990年3月11號 |
| 面積 | |
• 總計 | 65,300 km2(25,200 sq mi)(第121位) |
• 水域(%) | 1.98(2015年)[8] |
| 人口 | |
• 2021年估計 | 2,795,680[9](第137位) |
• 密度 | 43/km2(111.4/sq mi) |
| GDP(PPP) | 2021年估算 |
• 總計 | 1070億美元[10](第83位) |
• 人均 | 41,288美元[10](第34位) |
| GDP(國際匯率) | 2021年估算 |
• 總計 | 560億美元[10](第80位) |
• 人均 | 22,412美元[11](第54位) |
| 堅尼系數(%,2019年) | ▼ 35.4[12] 中 |
| HDI(2019年) | ▲ 0.882[13] 極高 · 第34位 |
| 貨幣 | 歐元(€)(EUR) |
| 時區 | UTC+2 (歐洲東部時間) |
• 夏令時(DST) | UTC+3 (歐洲東部夏令時間) |
| 日期格式 | yyyy-mm-dd (CE) |
| 行車方向 | 右 |
| 電話區號 | +370 |
| 互聯網頂級域 | .lt |
∗由於唔同嘅排名表計法未必一樣,上面嘅排名(第幾名/位)同個一覽表入面個排名未必一樣。 ∗IMF網站嘅人均GDP數字,同用GDP除以上面人口數得出嚟嘅數有可能唔一樣。 | |
立陶宛(立陶宛文:Lietuva)係東北歐波羅的海三國之一,北面係拉脫維亞,東南面係白俄羅斯,南面係波蘭,西南面同俄羅斯嘅加里寧格勒接壤,首都係維爾紐斯。原本係蘇聯加盟共和國,喺1990年自己宣佈獨立,去到第二年蘇聯至承認立陶宛獨立。佢係歐盟、北約、神根公約等等國際組織嘅成員。
歷史
[編輯]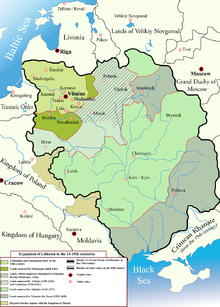
1253年,明道加斯加冕做立陶宛國王,1263年明道加斯被刺殺之後,立陶宛又變番做立陶宛大公國。14世紀嗰陣係歐洲最大嘅國家,領土範圍包括今日嘅立陶宛同白俄羅斯,同埋烏克蘭嘅大部分,以及波蘭同俄羅斯嘅一部分。1569年,立陶宛同波蘭一齊組成波蘭立陶宛聯邦。18世紀後期聯邦畀鄰國瓜分,立陶宛嘅地大部分畀俄羅斯佔據。第一次世界大戰之後,立陶宛共和國成立,去到1940年畀蘇聯佔領。1990年重新獨立。2004年立陶宛加入北大西洋公約組織同歐洲聯盟。
參考
[編輯]- ↑ "Lithuania's Constitution of 1992 with Amendments through 2019" (PDF). Constitute Project.
- ↑ "Rodiklių duomenų bazė - Oficialiosios statistikos portalas". osp.stat.gov.lt.
- ↑ "Population by religious community indicated, municipalities (2021)" (立陶宛文). Statistics Lithuania. 喺2 January 2022搵到.
- ↑ Kulikauskienė, Lina (2002). Lietuvos Respublikos Konstitucija [The Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania] (立陶宛文). Native History, CD. ISBN 978-9986-9216-7-7.
- ↑ Veser, Ernst (23 September 1997). "Semi-Presidentialism-Duverger's Concept – A New Political System Model" (PDF) (英文、中文). Department of Education, School of Education, University of Cologne. pp. 39–60. 原著 (PDF)喺2021年4月24號歸檔. 喺23 August 2017搵到.
Duhamel has developed the approach further: He stresses that the French construction does not correspond to either parliamentary or the presidential form of government, and then develops the distinction of 'système politique' and 'régime constitutionnel'. While the former comprises the exercise of power that results from the dominant institutional practice, the latter is the totality of the rules for the dominant institutional practice of the power. In this way, France appears as 'presidentialist system' endowed with a 'semi-presidential regime' (1983: 587). By this standard he recognizes Duverger's pléiade as semi-presidential regimes, as well as Poland, Romania, Bulgaria and Lithuania (1993: 87).
- ↑ Shugart, Matthew Søberg (September 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive and Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). Graduate School of International Relations and Pacific Studies. United States: University of California, San Diego. 原著 (PDF)喺19 August 2008歸檔. 喺23 August 2017搵到.
- ↑ Shugart, Matthew Søberg (December 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). French Politics. Palgrave Macmillan Journals. 3 (3): 323–351. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087. 原著 (PDF)喺4 March 2016歸檔. 喺23 August 2017搵到.
A pattern similar to the French case of compatible majorities alternating with periods of cohabitation emerged in Lithuania, where Talat-Kelpsa (2001) notes that the ability of the Lithuanian president to influence government formation and policy declined abruptly when he lost the sympathetic majority in parliament.
- ↑ "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). 喺2020-10-11搵到.
- ↑ "Pradžia – Oficialiosios statistikos portalas". osp.stat.gov.lt.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "Lithuania". International Monetary Fund.
- ↑ "World Economic Outlook Database". International Monetary Fund (IMF). 喺2022-02-07搵到.
- ↑ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey". ec.europa.eu. Eurostat. 喺12 September 2019搵到.
- ↑ "2020 Human Development Report". United Nations Development Programme. 2015. 喺24 March 2017搵到.
出面網頁
[編輯]維基語錄收錄咗同呢篇文相關嘅摘錄:
lt:Lietuva
- 立陶宛嘅官方網站
- Lietuva | Europos Sąjunga,歐洲聯盟 (立陶宛文)
- 〈国家概况 — 中华人民共和国外交部〉 (簡體中文)。中華人民共和國外交部。
- 〈立陶宛共和國 Republic of Lithuania - 歐洲地區 - 中華民國外交部 - 全球資訊網 Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of China (Taiwan)〉 (繁體中文)。中華民國外交部。
- "Lithuania - United States Department of State" (英文). 美國國務院.
- 立陶宛喺中央情報局《世界概況》嘅資料 (英文)
- 〈リトアニア共和国 | 外務省〉 (日文)。日本外務省。
- "Lithuania - Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade" (英文). 澳洲外交貿易部.




